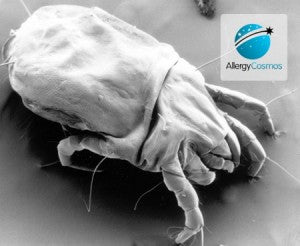
Dust Mite Allergy
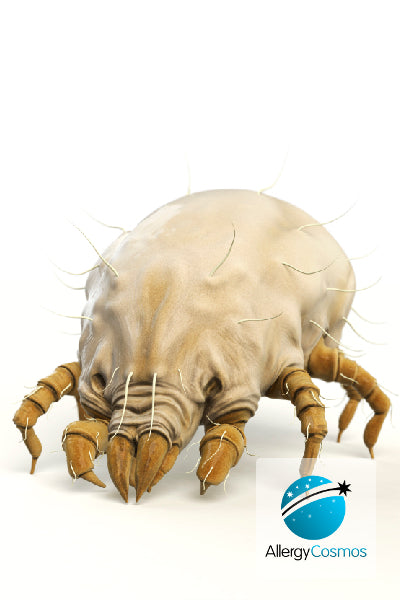
The house dust mite allergen is one of the most potent triggers of allergic reactions. More is known about house dust mite than any other allergen source because it is such a common trigger for rhinitis, asthma and eczema. This is good because we can give you lots of helpful tips and advice to practice allergen avoidance and to effectively control your dust mite allergies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are dust mites?
What is a dust mite allergy?
How common is dust mite allergy?
Where do dust mites lurk in my home?
What is the link between dust mite and humidity?
How can I get rid of dust mites in my home?
How can I get rid of dust mites with home improvements?
Should I use an anti-mite spray to get rid of them?
Is dust allergy always a result of house dust mite?
Related Products
-
Dust Mite Cleaning Products
Regular price £62.95Regular priceUnit price per -
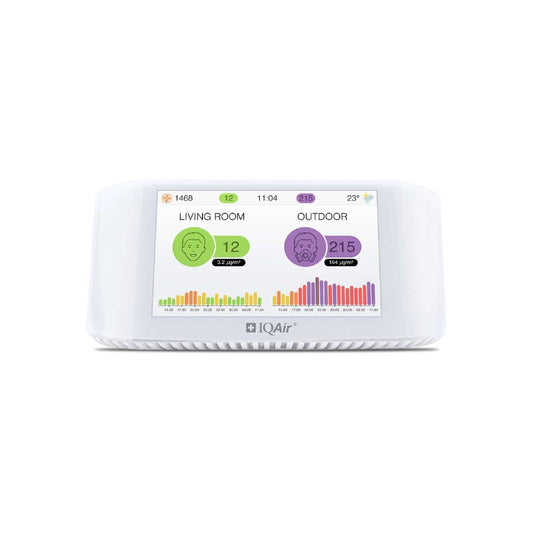
IQAir AirVisual Pro Air Quality Monitor
Regular price £274.00Regular priceUnit price per -
IQAir HealthPro 250 Air Purifier
Regular price £1,049.00Regular priceUnit price per -
Allersearch X-Mite Powder Carpet Cleaner
Regular price £24.95Regular priceUnit price per